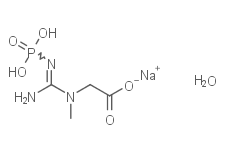
Creatine phosphate disodium salt
CAS No. 922-32-7
Creatine phosphate disodium salt( Disodium creatine phosphate )
Catalog No. M19262 CAS No. 922-32-7
Creatine phosphate is a phosphorylated creatine molecule that serves as a rapidly mobilizable reserve of high-energy phosphates in muscle, skeletal, and brain.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | 37 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 52 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 84 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameCreatine phosphate disodium salt
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionCreatine phosphate is a phosphorylated creatine molecule that serves as a rapidly mobilizable reserve of high-energy phosphates in muscle, skeletal, and brain.
-
DescriptionCreatine phosphate is a phosphorylated creatine molecule that serves as a rapidly mobilizable reserve of high-energy phosphates in muscle, skeletal, and brain.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsDisodium creatine phosphate
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number922-32-7
-
Formula Weight251.11
-
Molecular FormulaC4H8N3Na2O5P
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?H2O : 125 mg/mL (490.04 mM)
-
SMILESCN(CC(=O)O)C(=N)NP(=O)([O-])[O-].[Na+].[Na+]
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Schlattner, U et al. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease. 1762 (2): 164–180.
molnova catalog



related products
-
2F-Peracetyl-Fucose
2F-Peracetyl-Fucose (1,3,4-Tri-O-acetyl-2-deoxy-2-fluoro-L-fucopyranos) is a potent fucosyltransferase (FUT) inhibitor that suppresses salivary acidification and fucosylation in an in vitro inflammatory model.
-
Hecogenin
Hecogenin is a steroid saponin isolated from Agave sisalana. It is a selective inhibitor of human UDP-glucuronosyltransferases. Hecogenin has a wide spectrum of pharmacological activities including anti-inflammatory antifungal and gastroprotective effects.
-
Pelgifatamab
Pelgifatamab (BAY-2315497) is a prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) antibody with potential anticancer activity that can be used to study prostate cancer.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


